递归反转整个链表
实现代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 单链表节点的结构
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
对于递归算法,最重要的就是明确递归函数的定义。具体来说,reverse 函数定义是这样的: 输⼊⼀个节点 head ,将「以 head 为起点」的链表反转,并返回反转之后的头结点。
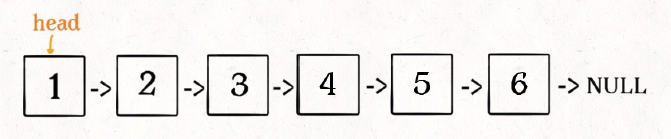
那么输⼊ reverse(head) 后,会在这⾥进⾏递归:
1
ListNode last = reverse(head.next);
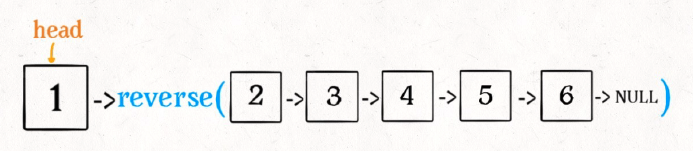
这个 reverse(head.next) 执⾏完成后,整个链表就成了这样:
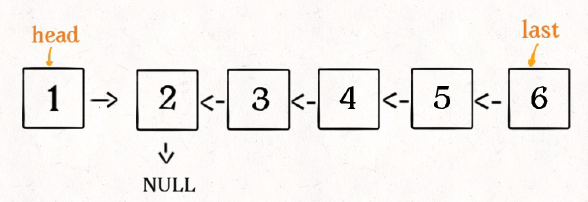
并且根据函数定义, reverse 函数会返回反转之后的头结点,⽤变量 last 接收了。
现在再来看下⾯的代码:
1
head.next.next = head;
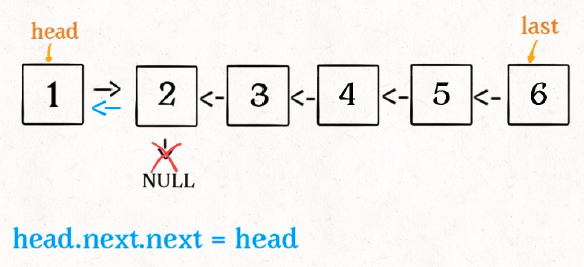
接下来:
1
2
head.next = null;
return last;
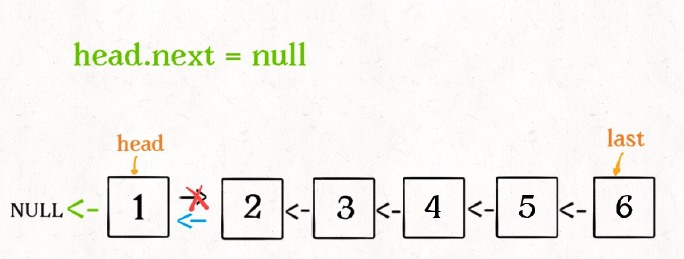
反转链表前 N 个节点
1
2
// 将链表的前 n 个节点反转(n <= 链表⻓度)
ListNode reverseN(ListNode head, int n)
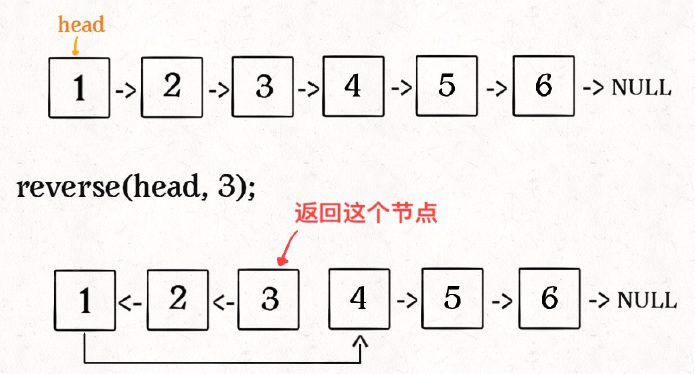
⽐如说对于下图链表,执⾏ reverseN(head, 3):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
ListNode successor = null; // 后驱节点
// 反转以 head 为起点的 n 个节点,返回新的头结点
ListNode reverseN(ListNode head, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
// 记录第 n + 1 个节点
successor = head.next;
return head;
}
// 以 head.next 为起点,需要反转前 n - 1 个节点
ListNode last = reverseN(head.next, n - 1);
head.next.next = head;
// 让反转之后的 head 节点和后⾯的节点连起来
head.next = successor;
return last;
}
具体的区别:
- base case 变为 n == 1 ,反转⼀个元素,就是它本⾝,同时要记录后驱 节点。
- 刚才我们直接把 head.next 设置为 null,因为整个链表反转后原来的 head 变成了整个链表的最后⼀个节点。但现在 head 节点在递归反转之 后不⼀定是最后⼀个节点了,所以要记录后驱 successor (第 n + 1 个节 点),反转之后将 head 连接上。