同步发送原理
RocketMQ 使用 Netty 进行发送,Netty 通讯默认都是异步的,那么同步是怎么实现的呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
// 1、定义一个 ResponseFuture 来处理响应结果
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
// 2、通过 Netty 执行完成后回调处理请求的结果
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
// 唤醒阻塞的线程
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
// 3、请求结果默认等待请求3秒钟,如果超过3秒则抛出异常。
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
1、定义一个 ResponseFuture 来处理响应结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class ResponseFuture {
//省略其它代码
......
private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
public RemotingCommand waitResponse(final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException {
this.countDownLatch.await(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this.responseCommand;
}
public void putResponse(final RemotingCommand responseCommand) {
this.responseCommand = responseCommand;
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
ResponseFuture 内部使用了 CountDownLatch 来实现的。当调用 waitResponse() 方法时阻塞当前线程,当返回结果时调用 putResponse() 方法存放结果,然后执行 this.countDownLatch.countDown() 唤醒阻塞的线程。
2、通过 Netty 执行完成后回调处理请求的结果
使用 Netty 进行发送消息,当 Netty 收到结果后会执行自定义的 ChannelFutureListener.operationComplete() 方法。
如果执行完成,调用 responseFuture.putResponse(null); 立即唤醒阻塞的线程,处理请求结果。
3、默认最长等待请求3秒钟,如果超过3秒则抛出异常
调用 responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis) 方法阻塞等待 Netty 返回结果。默认最长等待时间为 3 秒,如果超过 3 秒则认为调用超时,抛出 RemotingSendRequestException 异常信息。
异步发送原理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public void invokeAsyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
//1、尝试获得 semaphore 信号量,semaphore 默认为65535。
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreAsync.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreAsync);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl call timeout");
}
// 2、定义 ResponseFuture 来处理响应的结果
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
// 存储到把 ResponseFuture 存储到 responseTable 中。
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
// 3、调用 Netty 发送数据
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
// 3.1、成功则设置 responseFuture 的状态为发送成功
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
// 3.2、发送失败则快速处理失败请求
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <{}> failed.", RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel));
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
responseFuture.release();
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel) + "> Exception", e);
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info =
String.format("invokeAsyncImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreAsync.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreAsync.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
1、尝试获得 semaphore 信号量,semaphore 默认为 65535
1
2
public static final int CLIENT_ASYNC_SEMAPHORE_VALUE
=Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty(COM_ROCKETMQ_REMOTING_CLIENT_ASYNC_SEMAPHORE_VALUE, "65535"));
异步发送请求的并发量,默认最大为65535。
2、定义 ResponseFuture 来处理响应的结果
ResponseFuture responseFuture 定义了发送数据响应的结果,同上面介绍的同步发送。 把responseFuture 存储到 responseTable 中。
1
2
protected final ConcurrentMap<Integer /* opaque */, ResponseFuture> responseTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ResponseFuture>(256);
opaque 为请求的唯一标识,每次请求创建一个新的(AtomicInteger 自增的)。
3、调用 Netty 发送数据
调用 Netty 异步发送数据。
- Netty 发送成功则设置 responseFuture 的状态为发送成功
- 发送失败则快速处理失败请求
快速失败是相对下面的定时任务扫描处理响应结果的
处理异步的响应结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
//1、 定时间隔3秒钟扫描一次 responseTable
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingServer.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);
public void scanResponseTable() {
final List<ResponseFuture> rfList = new LinkedList<ResponseFuture>();
Iterator<Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture>> it = this.responseTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture> next = it.next();
ResponseFuture rep = next.getValue();
// 2、扫描开始执行时间大于 执行超时+1s 的 ResponseFuture 数据,并存放到 rfList 中
if ((rep.getBeginTimestamp() + rep.getTimeoutMillis() + 1000) <= System.currentTimeMillis()) {
rep.release();
it.remove();
rfList.add(rep);
log.warn("remove timeout request, " + rep);
}
}
// 3、执行处理完成或超时的请求
for (ResponseFuture rf : rfList) {
try {
executeInvokeCallback(rf);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("scanResponseTable, operationComplete Exception", e);
}
}
}
-
定时间隔3秒钟扫描一次 responseTable 当 Netty 客户端和服务端启动的时候,都会自动这个定时任务。定时的扫描 responseTable 的请求数据。每隔3秒扫描一次。
-
扫描开始执行时间大于 执行超时+1s 的 ResponseFuture 数据 Netty 请求的时候默认会有等待的执行超时时间(或可自己设置),超过超时时间的则认为任务超时,需要通过定时任务处理超时的任务。 异步执行完成的请求也会在定时任务中回调执行处理结果。
Oneway 发送
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public void invokeOnewayImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
request.markOnewayRPC();
// 尝试获得 semaphore 信号量,semaphore 默认为65535。
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreOneway.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreOneway);
try {
// 2、调用 Netty 发送请求
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
once.release();
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
once.release();
log.warn("write send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeOnewayImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info = String.format(
"invokeOnewayImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreOneway.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreOneway.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
1、尝试获得 semaphore 信号量,semaphore 默认为65535
1
2
public static final int CLIENT_ONEWAY_SEMAPHORE_VALUE
= Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty(COM_ROCKETMQ_REMOTING_CLIENT_ONEWAY_SEMAPHORE_VALUE, "65535"));
Oneway 方式发送请求的并发量,默认最大为65535。
2、调用 Netty 发送请求
这里只是发送数据,而没有处理响应结果。 这种方式发送数据,吞吐量更高,但不管数据是否发送成功。
问题
消息发送流程?
rocketMq通信协议是什么?
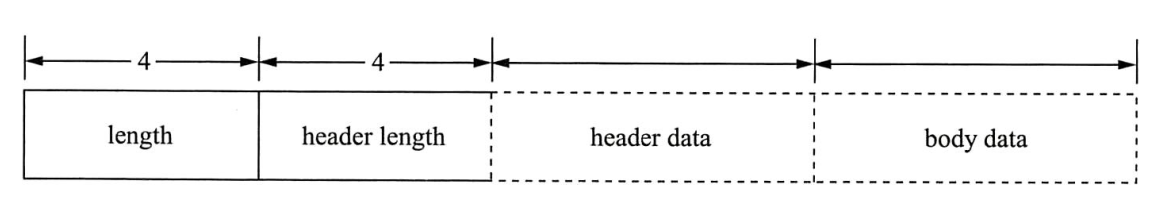 RocketMQ 设计了自己的一个通信协议,用于消息内容和二进制格式之间的转换:
RocketMQ 设计了自己的一个通信协议,用于消息内容和二进制格式之间的转换:
- length:4 字节整数,二三四部分长度总和;
- header length:4字节整数,第三部分header data长度;
- 最高8为存储header data的协议
- 底24位为数据长度
- header data:存放Json序列化的数据;
- body data:应用自定义二进制序列化的数据。
消息的编码过程
消息的编码是在 RemotingCommand 中 encode 方法中完成的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public ByteBuffer encode() {
// 1> header length size
int length = 4;
// 2> header data length
byte[] headerData = this.headerEncode();
length += headerData.length;
// 3> body data length
if (this.body != null) {
length += body.length;
}
ByteBuffer result = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 + length);
// 1.先放入消息的总大小
result.putInt(length);
// 2.再放入头部的长度
result.put(markProtocolType(headerData.length, serializeTypeCurrentRPC));
// 3.接着放入头部数据
result.put(headerData);
// 4.最后放入消息体的数据
if (this.body != null) {
result.put(this.body);
}
result.flip();
return result;
}
消息的解码过程
消息的解码是在类 RemotingCommand 中 decode方法中完成的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
int length = byteBuffer.limit();// 获取byteBuffer的总长度
int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();// 1.获取前4个字节,组装int类型,该长度为总长度 图中 length
int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);// length & 0xFFFFFF 获取消息头的长度,与运算,编码时候的长度即为24位
byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];// 保存header data
byteBuffer.get(headerData);// 2.从缓冲区中读取headerLength个字节的数据,这个数据就是报文头部的数据
RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));
int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;// 报文体的数据,减去了第二、三部分的长度
byte[] bodyData = null;
if (bodyLength > 0) {
bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuffer.get(bodyData);// 获取消息体的数据
}
cmd.body = bodyData;
return cmd;
}
rocketMQ 如何处理半包问题?
由于RocketMQ在消息头定义长度字段来标识消息总长度, 可用Netty提供的相应的解码器:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
大多数协议(私有或公有),协议头中会携带长度字段,用于标识消息体或者整包消息的长度,例如SMPP、HTTP协议等。由于基于长度解码需求的通用性,Netty提供了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,自动屏蔽TCP底层的拆包和粘包问题,只需要传入正确的参数,即可轻松解决”读半包”问题。
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder构造函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(ByteOrder byteOrder, // 标示字节流表示的数据是大端还是小端,用于长度域的读取;
int maxFrameLength, // 帧的最大长度,如果帧长度大于此值,抛异常;
int lengthFieldOffset, // 长度域的偏移量
int lengthFieldLength, // 长度域的长度;
int lengthAdjustment, // 该字段加长度字段等于数据帧的长度,包括长度调整的大小,长度域的数值表示的长度加上这个修正值表示的就是带header的包;
int initialBytesToStrip, // 从数据帧中跳过的字节数,表示获取完一个完整的数据包之后,忽略前面的指定的位数个字节,应用解码器拿到的就是不带长度域的数据包;
boolean failFast // 如果为true,则表示读取到长度域,TA的值的超过maxFrameLength,就抛出一个 TooLongFrameException,而为false表示只有当真正读取完长度域的值表示的字节之后,才会抛出 TooLongFrameException,默认情况下设置为true,建议不要修改,否则可能会造成内存溢出。
) {
}
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 定义了一个长度字段来表示消息的长度,因此能够处理可变长度的消息。将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头固定位置增加一个表示长度的字段,通过长度字段来获取整包的信息。LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder继承了ByteToMessageDecoder,即转换字节这样的工作是由ByteToMessageDecoder来完成,而LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder只用安心完成他的解码工作就好。