摘自:知乎
反射(Reflection) 是 Java 程序语言的特征之一,它允许运行中的 Java 程序获取自身的信息,并且可以操作类或对象的内部属性。通过反射机制,可以在运行时访问 Java 对象的属性,方法,构造方法等。
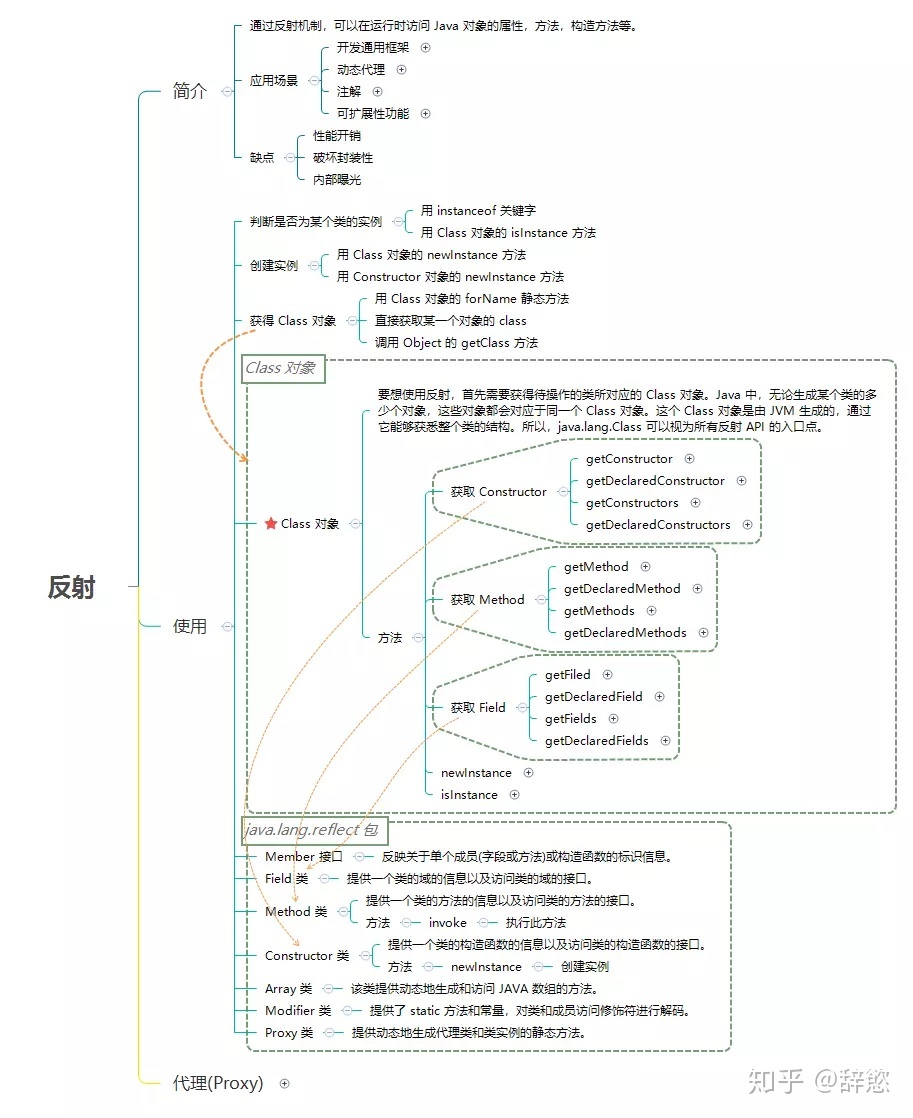
应用场景
- 开发通用框架 - 反射最重要的用途就是开发各种通用框架。很多框架(比如 Spring)都是配置化的(比如通过 XML 文件配置 JavaBean、Filter 等),为了保证框架的通用性,它们可能需要根据配置文件加载不同的对象或类,调用不同的方法,这个时候就必须用到反射——运行时动态加载需要加载的对象
- 动态代理 - 在切面编程(AOP)中,需要拦截特定的方法,通常,会选择动态代理方式。这时,就需要反射技术来实现了。
- 注解 - 注解本身仅仅是起到标记作用,它需要利用反射机制,根据注解标记去调用注解解释器,执行行为。如果没有反射机制,注解并不比注释更有用。
- 可扩展性功能 - 应用程序可以通过使用完全限定名称创建可扩展性对象实例来使用外部的用户定义类。
缺点
- 性能开销 - 由于反射涉及动态解析的类型,因此无法执行某些 Java 虚拟机优化。因此,反射操作的性能要比非反射操作的性能要差,应该在性能敏感的应用程序中频繁调用的代码段中避免。
- 破坏封装性 - 反射调用方法时可以忽略权限检查,因此可能会破坏封装性而导致安全问题。
- 内部曝光 - 由于反射允许代码执行在非反射代码中非法的操作,例如访问私有字段和方法,所以反射的使用可能会导致意想不到的副作用,这可能会导致代码功能失常并可能破坏可移植性。反射代码打破了抽象,因此可能会随着平台的升级而改变行为。
反射机制
java.lang.reflect 包 Java 中的 java.lang.reflect 包提供了反射功能。java.lang.reflect 包中的类都没有 public 构造方法。 java.lang.reflect 包的核心接口和类如下:
- Member 接口 - 反映关于单个成员(字段或方法)或构造函数的标识信息。
- Field 类 - 提供一个类的域的信息以及访问类的域的接口。
- Method 类 - 提供一个类的方法的信息以及访问类的方法的接口。
- Constructor 类 - 提供一个类的构造函数的信息以及访问类的构造函数的接口。
- Array 类 - 该类提供动态地生成和访问 JAVA 数组的方法。
- Modifier 类 - 提供了 static 方法和常量,对类和成员访问修饰符进行解码。
- Proxy 类 - 提供动态地生成代理类和类实例的静态方法。
获得 Class 对象
- 使用 Class 类的 forName 静态方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
package io.github.dunwu.javacore.reflect;
public class ReflectClassDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("io.github.dunwu.javacore.reflect.ReflectClassDemo01");
System.out.println(c1.getCanonicalName());
Class c2 = Class.forName("[D");
System.out.println(c2.getCanonicalName());
Class c3 = Class.forName("[[Ljava.lang.String;");
System.out.println(c3.getCanonicalName());
}
}
//Output:
//io.github.dunwu.javacore.reflect.ReflectClassDemo01
//double[]
//java.lang.String[][]
使用类的完全限定名来反射对象的类。常见的应用场景为:在 JDBC 开发中常用此方法加载数据库驱动。
直接获取某一个对象的 class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class ReflectClassDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boolean b;
// Class c = b.getClass(); // 编译错误
Class c1 = Boolean.class;
System.out.println(c1.getCanonicalName());
Class c2 = java.io.PrintStream.class;
System.out.println(c2.getCanonicalName());
Class c3 = int[][][].class;
System.out.println(c3.getCanonicalName());
}
}
//Output:
//boolean
//java.io.PrintStream
//int[][][]
调用 Object 的 getClass 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
package io.github.dunwu.javacore.reflect;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class ReflectClassDemo03 {
enum E {
A, B
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c = "foo".getClass();
System.out.println(c.getCanonicalName());
Class c2 = ReflectClassDemo03.E.A.getClass();
System.out.println(c2.getCanonicalName());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
Class c3 = bytes.getClass();
System.out.println(c3.getCanonicalName());
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
Class c4 = set.getClass();
System.out.println(c4.getCanonicalName());
}
}
//Output:
//java.lang.String
//io.github.dunwu.javacore.reflect.ReflectClassDemo.E
//byte[]
//java.util.HashSet
创建实例
通过反射来创建实例对象主要有两种方式:
- 用 Class 对象的 newInstance 方法。
- 用 Constructor 对象的 newInstance 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class NewInstanceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class<?> c1 = StringBuilder.class;
StringBuilder sb = (StringBuilder) c1.newInstance();
sb.append("aaa");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//获取String所对应的Class对象
Class<?> c2 = String.class;
//获取String类带一个String参数的构造器
Constructor constructor = c2.getConstructor(String.class);
//根据构造器创建实例
String str2 = (String) constructor.newInstance("bbb");
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
//Output:
//aaa
//bbb
Field
Class 对象提供以下方法获取对象的成员(Field):
- getFiled - 根据名称获取公有的(public)类成员。
- getDeclaredField - 根据名称获取已声明的类成员。但不能得到其父类的类成员。
- getFields - 获取所有公有的(public)类成员。
- getDeclaredFields - 获取所有已声明的类成员。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class ReflectFieldDemo {
class FieldSpy<T> {
public Boolean[][] b = null;
public String name = "Alice";
public List<Integer> list;
public T val;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field f1 = FieldSpy.class.getField("b");
System.out.format("Type: %s%n", f1.getType());
Field f2 = FieldSpy.class.getField("name");
System.out.format("Type: %s%n", f2.getType());
Field f3 = FieldSpy.class.getField("list");
System.out.format("Type: %s%n", f3.getType());
Field f4 = FieldSpy.class.getField("val");
System.out.format("Type: %s%n", f4.getType());
}
}
//Output:
//Type: class [[Z
//Type: class java.lang.String
//Type: interface java.util.List
//Type: class java.lang.Object
Method
Class 对象提供以下方法获取对象的方法(Method):
- getMethod - 返回类或接口的特定方法。其中第一个参数为方法名称,后面的参数为方法参数对应 Class 的对象。
- getDeclaredMethod - 返回类或接口的特定声明方法。其中第一个参数为方法名称,后面的参数为方法参数对应 Class 的对象。
- getMethods - 返回类或接口的所有 public 方法,包括其父类的 public 方法。
- getDeclaredMethods - 返回类或接口声明的所有方法,包括 public、protected、默认(包)访问和 private 方法,但不包括继承的方法。
获取一个 Method 对象后,可以用 invoke 方法来调用这个方法,invoke 方法的原型为:
1
2
3
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class ReflectMethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
// 返回所有方法
Method[] methods1 = System.class.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println("System getDeclaredMethods 清单(数量 = " + methods1.length + "):");
for (Method m : methods1) {
System.out.println(m);
}
// 返回所有 public 方法
Method[] methods2 = System.class.getMethods();
System.out.println("System getMethods 清单(数量 = " + methods2.length + "):");
for (Method m : methods2) {
System.out.println(m);
}
// 利用 Method 的 invoke 方法调用 System.currentTimeMillis()
Method method = System.class.getMethod("currentTimeMillis");
System.out.println(method);
System.out.println(method.invoke(null));
}
}
Constructor
Class 对象提供以下方法获取对象的构造方法(Constructor):
- getConstructor - 返回类的特定 public 构造方法。参数为方法参数对应 Class 的对象。
- getDeclaredConstructor - 返回类的特定构造方法。参数为方法参数对应 Class 的对象。
- getConstructors - 返回类的所有 public 构造方法。
- getDeclaredConstructors - 返回类的所有构造方法。 获取一个 Constructor 对象后,可以用 newInstance 方法来创建类实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class ReflectMethodConstructorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
Constructor<?>[] constructors1 = String.class.getDeclaredConstructors();
System.out.println("String getDeclaredConstructors 清单(数量 = " + constructors1.length + "):");
for (Constructor c : constructors1) {
System.out.println(c);
}
Constructor<?>[] constructors2 = String.class.getConstructors();
System.out.println("String getConstructors 清单(数量 = " + constructors2.length + "):");
for (Constructor c : constructors2) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("====================");
Constructor constructor = String.class.getConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor);
String str = (String) constructor.newInstance("bbb");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Array
数组在 Java 里是比较特殊的一种类型,它可以赋值给一个对象引用。下面我们看一看利用反射创建数组的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class ReflectArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
Object array = Array.newInstance(cls, 25);
//往数组里添加内容
Array.set(array, 0, "Scala");
Array.set(array, 1, "Java");
Array.set(array, 2, "Groovy");
Array.set(array, 3, "Scala");
Array.set(array, 4, "Clojure");
//获取某一项的内容
System.out.println(Array.get(array, 3));
}
}
//Output:
//Scala
其中的 Array 类为 java.lang.reflect.Array 类。我们通过 Array.newInstance 创建数组对象,它的原型是:
1
2
3
4
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length)
throws NegativeArraySizeException {
return newArray(componentType, length);
}