BIO
BIO 的服务器通信模型:
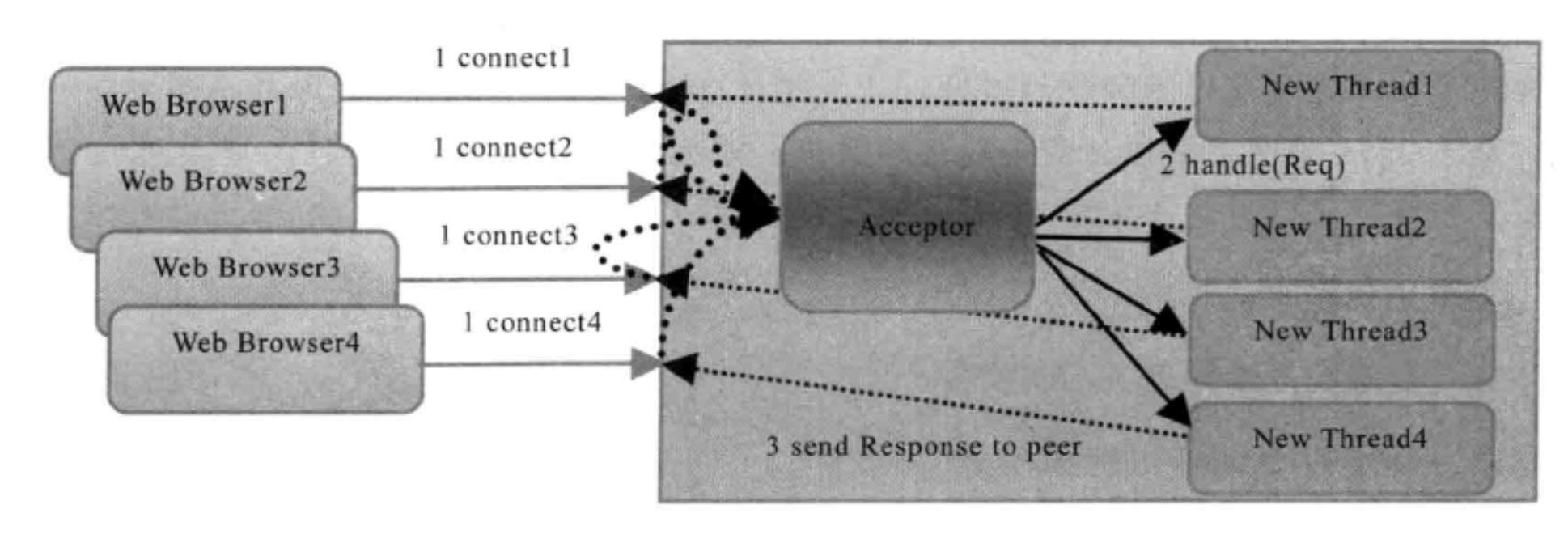 由一个独立的 Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理,处理完成之后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。
由一个独立的 Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理,处理完成之后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。
InputStream 是Java标准库提供的最基本的输入流。它位于java.io这个包里。java.io包提供了所有同步IO的功能,它是所有输入流的超类。这个抽象类定义的一个最重要的方法就是int read(),签名如下:
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
这个方法会读取输入流的下一个字节,并返回字节表示的int值(0~255)。如果已读到末尾,返回-1表示不能继续读取了。
在读取流的时候,一次读取一个字节并不是最高效的方法。很多流支持一次性读取多个字节到缓冲区,对于文件和网络流来说,利用缓冲区一次性读取多个字节效率往往要高很多。InputStream提供了两个重载方法来支持读取多个字节:
int read(byte[] b);//读取若干字节并填充到byte[]数组,返回读取的字节数int read(byte[] b, int off, int len);//指定byte[]数组的偏移量和最大填充数
利用上述方法一次读取多个字节时,需要先定义一个byte[]数组作为缓冲区,read()方法会尽可能多地读取字节到缓冲区, 但不会超过缓冲区的大小。read()方法的返回值不再是字节的int值,而是返回实际读取了多少个字节。如果返回-1,表示没有更多的数据了。
实例
服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
ServerSocket server = null;
try {
server = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("The time server is start in port : " + port);
Socket socket = null;
while (true) {
socket = server.accept();
new Thread(new TimeServerHandler(socket)).start();
}
} finally {
if (server != null) {
System.out.println("The time server close");
server.close();
server = null;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| public class TimeServerHandler implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public TimeServerHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
this.socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(this.socket.getOutputStream(), true);
String currentTime;
String body;
while (true) {
body = in.readLine();
if (body == null)
break;
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body);
currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
out.println(currentTime);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
if (this.socket != null) {
try {
this.socket.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
this.socket = null;
}
}
}
}
|
客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
Socket socket = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", port);
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
out.println("QUERY TIME ORDER");
System.out.println("Send order 2 server succeed.");
String resp = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Now is : " + resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
in = null;
}
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
}
}
|
 由一个独立的 Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理,处理完成之后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。
由一个独立的 Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理,处理完成之后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。